Relative Position
Exercise
- In the "index.html" file, replace the code with the following:
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>CSS</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="./css/styles.css"> </head> <body> <h1>Relative Position</h1> <div> <p class="static-position">This paragraph has a static position which is the default.</p> <p class="no-position">This paragraph has a static position (no css property necessary).</p> </div> <div> <p class="relative-position-top">This paragraph has a relative position shifted 10px down from the top.</p> <p class="no-position">This paragraph has a static position (no css property necessary).</p> </div> <div> <p class="relative-position-bottom-left">This paragraph has a relative position shifted 10px up from the bottom and 1rem from the left.</p> <p class="no-position">This paragraph has a static position (no css property necessary).</p> </div> </body> </html>
- Save.
- If "Live Server" is not already running, right-click anywhere in the editor and select "Open with Live Server" from the context menu.
- In the "styles.css" file, replace the code with the following:
div { border: 5px solid blue; padding: 10px; margin: 5px; } .no-position { background: blue; color: white; } .static-position { background: red; position: static; } .relative-position-top { background: red; position: relative; top: 10px; } .relative-position-bottom-left { background: red; position: relative; bottom: 10px; left: 1rem; }
- Save.
- In the browser, you should see the following:
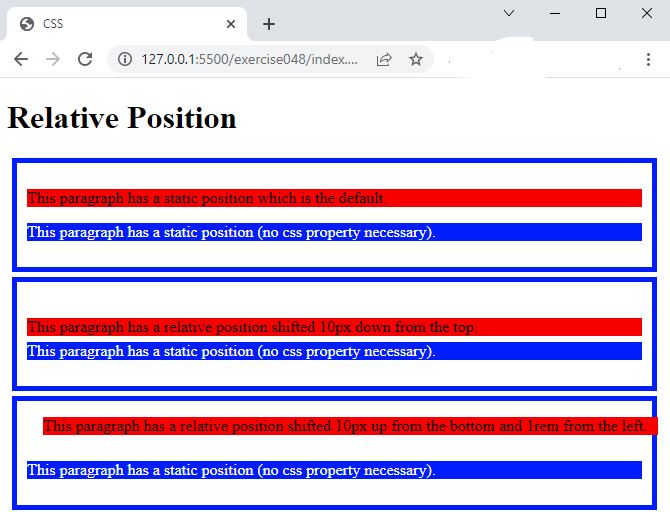
Code Walkthrough and Explanation
position
In CSS, relative positioning is a type of positioning that enables an element to be positioned relative to its
normal
position on the page or relative to its parent container. When an element is relatively positioned, it is moved
from
its original position using the top, bottom, left, or right
properties, while still maintaining its space in the document flow. This means that other elements on the page
are not
affected by the relative positioning of an element. The relative position of an element is determined by the
position
of its nearest positioned ancestor. If no positioned ancestor exists, the element will be positioned relative to
the
initial containing block of the document.
top
In CSS, the top property specifies the distance between the top edge of a positioned element and
the top
edge of its containing block. It is used to position an element relative to its containing block or to another
positioned element. When an element has a position property of relative,
absolute, or fixed, the top property can be used to move the element up
or
down. The value of the top property can be specified in pixels, ems, rems, percentages, or any other valid
length
unit. By default, the value of the top property is auto, which means the element is positioned at
the top
of its containing block.
bottom
In CSS, the bottom property is used to specify the distance between the bottom edge of a
positioned
element and the bottom edge of its containing block. It is one of the properties that can be used in conjunction
with
the position property, which is used to set the positioning method of an element on a web page.
When the
position property is set to absolute or fixed, the bottom property can be
used
to move the element up or down relative to its containing block. For example, setting bottom: 20px
would
move the element 20 pixels up from the bottom edge of its containing block. If the position
property is
set to relative, the bottom property can also be used to adjust the position of the element, but it
will
be relative to its initial position rather than the bottom edge of its containing block.
left
In CSS, the left property sets the left edge of an element's box to a specified position
relative
to the left edge of the nearest positioned ancestor element or the containing block if there is no positioned
ancestor. The value can be specified in various units, such as pixels, percentages, or ems. The
left
property is commonly used along with the position property to position an element precisely on a
page.
When used in combination with position: absolute or position: fixed, the
left
property can be used to create a layout where an element is positioned relative to the left edge of the browser
window
or its nearest positioned ancestor.
right
In CSS, the right property is used to set the distance of an element's right edge from the
right
edge of its containing block. It can be used to position an element relative to its containing block, along with
the
position property. For example, setting the right property to 10px will move the
element 10
pixels away from the right edge of its containing block. If the position property is not set, the
right
property will have no effect. The right property is often used in combination with the
left
property to horizontally position an element within its containing block.
Experiment with the Code
- Try adding your own
<p>to an existing<div>andpositionit to the bottom right corner.
Video and Code References
Questions? Subscribe and ask in the video comments: