Fixed Position
Exercise
- In the "index.html" file, replace the code with the following:
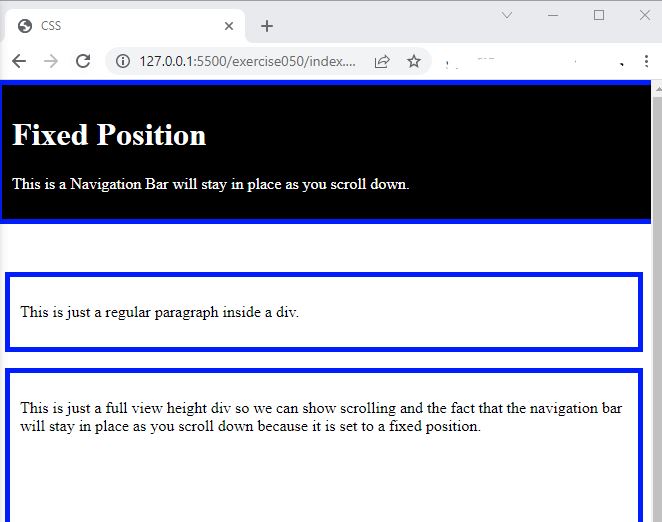
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>CSS</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="./css/styles.css"> </head> <body> <div class="navbar"> <h1>Fixed Position</h1> <p>This is a Navigation Bar will stay in place as you scroll down.</p> </div> <div> <p>This is just a regular paragraph inside a div.</p> </div> <div class="full-vh"> <p>This is just a full view height div so we can show scrolling and the fact that the navigation bar will stay in place as you scroll down because it is set to a fixed position.</p> </div> </body> </html>
- Save.
- If "Live Server" is not already running, right-click anywhere in the editor and select "Open with Live Server" from the context menu.
- In the "styles.css" file, replace the code with the following:
div { border: 5px solid blue; padding: 10px; margin-top: 20vh; } .navbar { position: fixed; top: 0; left: 0; margin: 0; width: 100vw; color: white; background: black; } .full-vh { height: 100vh; margin-top: 1rem; }
- Save.
- In the browser, you should see the following:
Code Walkthrough and Explanation
position: fixed;
The position: fixed; property in CSS is used to position an element on a web page relative to the
browser window, rather than relative to its parent container or the document flow. This means that an element
with
position: fixed; will remain in a fixed position even when the user scrolls the page. This can be
useful
for creating persistent elements on a web page, such as a navigation menu or a social media sharing bar, that
should
always be visible to the user. The position of the fixed element is specified using the top,
bottom, left, and right properties.
Experiment with the Code
- Try adding a
<div>that is fixed to the bottom of the page.
Video and Code References
Questions? Subscribe and ask in the video comments: