DIV and SPAN Elements
Exercise
- In the "index.html" file, replace the code with the following:
<html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0"> <title>CSS</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="./css/styles.css"> </head> <body> </body> </html>
- Save.
- If "Live Server" is not already running, right-click anywhere in the editor and select "Open with Live Server" from the context menu.
- Add a two "div" elements between the opening and closing body tags:
<div> </div> <div> </div>
- Save.
- Add an "h3" header and a paragraph with a "span" element between the opening and closing tag of the first "div" element:
<h3>Section 1</h3> <p>CSS <span>makes</span> the website look good</p>
- Save.
- Add an "h3" header and a paragraph with a "span" element between the opening and closing tags of the second "div" element:
<h3>Section 2</h3> <p>List of <span>things</span> I'm learning</p>
- Save.
- In the "styles.css" file, replace the code with the following:
div { color: blue; } span { color: black; font-weight: bold; }
- Save.
- In the browser, you should see the following:
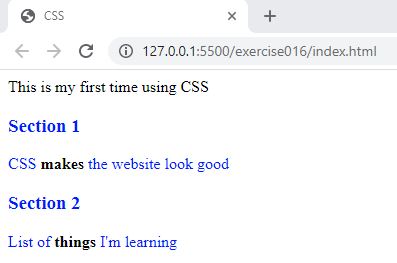
Code Walkthrough and Explanation
<div></div>
A div is a block level HTML element that is commonly used as a container for other elements. It is
short
for "division" and serves as a way to divide up a web page into distinct sections. The
div
element does not have any inherent styling but it can be styled using CSS and it can be used to group elements
together for the purpose of applying styles, organizing the layout, or creating a specific structure. The
div element can be thought of as a blank canvas that can be shaped an molded to fit the needs of a
particular website.
<span></span>
In HTML, a <span> element is an inline container used to apply styles to a small section of
text
rather than the entire block-level container, like <div>. It is often used to apply styles to
specific words or phrases within a block of text such as making certain words bold, italic, or underlined.
In HTML, elements can be either inline or block-level elements. This distinction determines how the elements are displayed on a webpage.
- Inline elements occupy only the space necessary to display the content and they do not start a new line
after the
element. Examples of inline elements include the
<a>,<span>, and<img>tags. - Block-level elements occupy the full width of the parent container and they create a new line after the
element.
Examples of block-level elements include the
<div>,<h1>, and<p>tags.
It's important to understand the distinction between inline and clock-level elements because it affects the layout of a webpage.
font-weight: bold;
font-weight is a CSS property that specifies the weight, or thickness of the font used to render
text.
This property can be set to one of several values, including keywords like normal or
bold,
or a numerical value between 100 and 900 (with 400 representing normal weight and 700 representing bold). The
value of
font-weight determines how thick the text appears on the page, with higher values resulting in
thicker,
heavier text.
Experiment with the Code
- Try adding another
<div>block to the HTML. - Try adding another
<span>, give it an id, and addcssselector for the id to make the colorgreen.
Video and Code References
Questions? Subscribe and ask in the video comments: